- When measuring volts it needs to be connected in parallel.
- When measuring amps it needs to be connected in series.
This was a place I shared my learning up to December 2021.From 2022 onwards I used a different blog platform.
Tuesday, December 1, 2020
Voltmeter and Ammeter | Physics
Tuesday, November 24, 2020
Circuits
Tuesday, November 17, 2020
Circuits | Physics
Activity:
Go on to the PHET website and click on LAB: https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/circuit-construction-kit-dc/latest/circuit-construction-kit-dc_en.html
I want you to construct a few different circuits, try to make them and then take a screenshot of them and post the pic here.
A circuit containing a battery, a light bulb, connected by wires:
Now add a switch into the circuit you just made, what happens when the switch is open or closed?
Now click on the battery and increase the voltage it supplies to the circuit. What happened?
Underneath the switch there is an arrow, scroll through the options to the end and try putting some random things into the circuit like a coin or dog. What happens to light bulbs?
Friday, November 13, 2020
Circuit | Physics
Activity:
Go on to the PHET website and click on LAB: https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/circuit-construction-kit-dc/latest/circuit-construction-kit-dc_en.html
I want you to construct a few different circuits, try to make them and then take a screenshot of them and post the pic here.
A circuit containing a battery, a light bulb, connected by wires:
Now add a switch into the circuit you just made, what happens when the switch is open or closed?
Wednesday, November 11, 2020
Electricity Circuits
There are two forms of circuits; Series and Parallel.
Houses have Parallel circuits are found in houses. If one bulb blows out, then the rest of them are on.
 |
| Series Circuit Credit: https://sites.google.com/site/lamsnc2dvella/Home/grade-9e-science/unit-3---electricity/series-and-parallel-circuit |
 |
| Parallel Circuit Credit: https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/textbook/direct-current/chpt-5/what-are-series-and-parallel-circuits/ |
Parallel
Series
Wednesday, November 4, 2020
Electricity | Physics
Van de Graaff generator generates static electricity.
Activity:
1 - Fill in the table
Static electricity | Current electricity | |
What is it caused by? | When there is an imbalance between negative and positive charges within or on the surface of a material. | It can be generated when a moving metal wire through a magnetic field. |
Do the negative charges move? | Yes | No |
Does it power appliances? | No | Yes |
2 - What are some examples of static electricity:
Carpet
Lightning
Trampoline
Hair
Write up for a Van der Graaff experiment:
How does the Van der Graaff machine work?
The Van der Graaff machine pulls electrons, moves them along a belt and stores them on the large sphere. These electrons repel each other and try to get as far away from each other as possible, spreading out on the surface of the sphere.What was one of the experiments they did with the machine?
Putting your hand on the Van der Graaff machine and waiting for your hair to stick up.Describe what happened, what did you see?
After some time, the hair sticked up which looked cool. But, when the machine stopped then the hair goes back to normal.Why did you see this happen?
Tuesday, November 3, 2020
The Eye - Conclusion
The Eye
Section 1: Label the diagram of the eye.
- Sclera
- lens
- Iris
- Cornea
- Retina
- Pupil
- Optic Nerve
Section 2: Complete the optical illusions and write down how you think each optical illusion works.
Young
Yes
Neither, both are the same size
Two faces and then see a white vase
Small is bigger
See three blocks of rectangle prism.
Can see white arrows going up and down and lines of black as well
A line with various arrows
A staircase
Blocks of rectangles
Two blocks
Various optical illusion triangle
One circle with another line dotted around and another circle where the dotted line is inside
Many shapes
Section 3: Find 10 interesting facts about the eye.
Your eye focuses on 50 different objects every second.
Your eyes can see approximately 10 million different colours.
It is impossible to sneeze with your eyes open.
80% of all learning comes through your eyes.
An average person blinks 12 times a minute.
The optic nerve contains more than one million nerve cells.
On average, you will blink approximately 4,200,000 times in a single year.
80% of our memories are determined by what we see.
A blink typically lasts 100-150 milliseconds.
If the human eye was a digital camera, it would have 576 megapixels.
Section 4: Colour Blindness Eye test
What are your colour blind test results?
Inconclusive
What does this mean?
Fine
What is normal colour vision?
It uses all three types of light cones correctly and is known as trichromacy.
Wednesday, October 28, 2020
Eye Dissection | Physics
Aim: To Dissect a cows eye and look at the different parts of the eye.
Equipment:
- A cows eye
- Scissors
- Tweezers
- Rubber Gloves
 |
| Before Dissection |
- Set up a treat with newspaper on the desk, the tray on top and the scissors and tweezers in the tray.
- Put on a rubber glove.
- Start to remove the excess fat and meat from around the eyeball before dissecting it.
- Puncture a hole in the cornea where the cornea and the sclera meet.
- Cut around the cornea so that the vitreous fluid leaks out of the eye onto the tray.
- Once the cornea has been totally removed you will be able to remove the lens from the iris.
- Cut the eye un half so that the inside is totally exposed. Once this has been done you will be able to access the retina at the back of the eye.
- You should now have placed the retina, lens, cornea and iris on a piece of paper.
- The dissection is not completed and all the parts of the eye need to be wrapped up and trashed. The trays and utensils that were needed must be rinsed and the rubber gloves thrown out.
 |
| After Dissection |
The Eye | Physics
Yesterday, we looked at the eye and writing the purpose of that part of the eye.
Part of eye | Purpose |
Retina | The retina is located at the back of the eye, and when light hits the retina, it activates two types of cells, rods and cones. Rods identify light and dark and support images under dark and dim conditions. Cones are responsible for colour vision - red, green and blue, which detects a range of wavelengths, not the three specific colours. |
Pupil | The size of the pupil determined by the iris, as the pupil gets bigger, as more light enters the eye. |
Cornea | Light goes through the cornea, the transparent outer covering of the eye. Because the eyeball is round, the cornea acts as a lens, it bends or refracts light. |
Optic Nerve | Where it sends light to the brain. |
Iris | Light travels through the cornea and aqueous humour (helps to shape the cornea and provides nourishment to the eye. |
Lens | Allows the eye to focus on either near and distant objects. |
Vitreous humour | Is a clear watery gel that helps the eye and allows for this distance. |
Wednesday, October 21, 2020
Curved Mirrors | Physics
There are three main types of mirrors in the laboratory. Plane mirrors are flat, convex and concave mirrors are both curved mirrors.
 |
| Types of Spherical Mirrors | BYJU'S Credit: https://byjus.com/physics/concave-and-convex-mirrors-spherical-mirrors/ |
Concave mirrors have the shiny surface on the inside of the curve. When looking at a tablespoon, the bowl of the spoon is concave.
Observing Reflection in Curved Mirrors
- Ray box
- Triple-set ray slide
- Concave and convex mirrors
- Power supply
- Set up your ray box, triple-set ray slide and power supply.
- Place the mirrors as indicated on the images below. Place the ray box at the top of the page and shine the 3 rays of light at the mirror.
- Ensure that the middle ray of light is hitting the mirror at a 90° angle.
- Carefully trace the direction of the three incident rays and the three reflected rays.
 |
| Concave Mirror |
 |
| Convex Mirror |
Reflection and Refraction | Physics
Complete the sentences using the following keywords:
Reflection light reflected normal same incidence
When light hits a mirror, the angle at which it hits is the incidence as the angle at which it is reflected. Scientists called this the Law of Reflection. In correct science terms, the Reflection Law states that the angle of normal is equal to the angle of same when measured from the reflection.
Diagram
Research Task
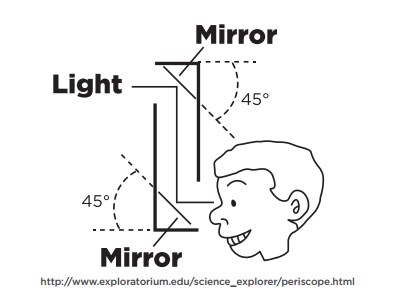
What is a periscope?
Is an instrument to see over, around or through an object which is above the level of direct sight. A periscope consists mainly of a tube with an arrangement of prisms or mirrors, and usually, lenses - used especially in submarines.How does it work?
Mirrors are placed at a 45° angle because light always reflects away from a mirror at the same angle that it hits it. There are usually two mirrors in a periscope.
 |
| Simple Periscope |
Draw and label a periscope?
Refraction Through Lenses | Physics
One of the most important uses of reflection involves lenses. By controlling how much, and in what direction, light bends we are able to see, heat objects and send information. A lens is simply a refracting object with a curved surface. The two main types of lenses are convex and concave.
Investigating Refraction Through Lenses
- Triple-split ray slide
- Power supply
- Concave lens
- Convex lens
- Set up a ray box, triple-slit ray slide and power supply.
- Place the convex lens and place the ray box near the convex lens, and shine the three rays of light at the lens. Make sure the central light hits the lens at 90° as indicated in the diagram.
- Carefully trace the direction of the incoming ray and refracted rays.
- Repeat using the concave lens.
 |
| Convex Lens |
 |
| Convex Lens |
 |
| Concave Lens |
 |
| Concave Lens |
Wednesday, October 14, 2020
Speed of Light | Physics
Speed of Light - 300,000,000 m/s
- Lightbox
- Power Supply
- Mirror
- Collect a ray box power supply and single-slit ray slide from your teacher, and set them up to produce a single beam of light.
- Place a plane mirror on the diagram of the protractor.
- Vary the angle of incidence and record the angle of reflection.
Angle of Incidence | Angle of Reflection |
0° | 0° |
10° | 20° |
20° | 30° |
30° | 40° |
40° | 50° |
50° | 60° |
60° | 70° |
70° | 70° |
80° | 80° |
- Complete the following sentences using the word list below.