 |
| Left: Spiral Galaxy Centre: Elliptical Galaxy Right: Irregular Galaxy |
Spiral Galaxy
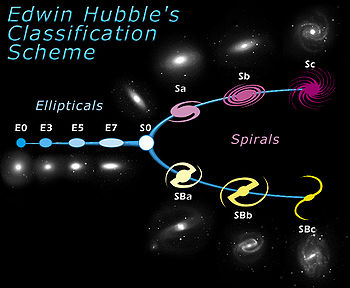 |
| The Hubble Sequence |
In 1926, Edwin Hubble came up a system to classify galaxies. Known as the Hubble Sequence, it organises galaxies base on their shape.
Spiral galaxies make up about 77 percent of the galaxies. Spiral galaxies are filled with gas and dust, which results in a wealth of a star formation. They are considered to be younger than elliptical galaxies, which contains less dust and form fewer stars. The twisted galaxies range from a billion to a trillion times as massive as the sun. The largest known spiral galaxy is NGC 6872, about 5 times the size of the Milky Way. The oldest observed spiral galaxy BX442 is about 10.7 billion years old. Because of the distance and the amount of time to travel, scientists are about to see the galaxy only 3 billion years after the Big Bang formed in the universe.
Elliptical Galaxy
 In 1926, Edwin Hubble came up a system to classify galaxies. Known as the Hubble Sequence, it organises galaxies base on their shape. Galaxies classified as E0 Galaxy appear to be almost perfect circles (ellipse). Elliptical galaxies have a broader range size than other types of galaxies. The smallest galaxies are dwarf elliptical galaxies, which is less than 10 percent the size of the Milky Way, and could contain only 10 million times the mass of the sun. Some ellipticals can also be stretched to more than a million light-years across, that can contain more than ten trillion stars. M87 (Messier 87) is identified as one of the largest galaxies in the universe. But astronomers have found more spiral galaxies than elliptical galaxies. As spiral galaxies are bright, elliptical galaxies are dim. Elliptical galaxies contain less gas and dust, which means few new stars are born.
In 1926, Edwin Hubble came up a system to classify galaxies. Known as the Hubble Sequence, it organises galaxies base on their shape. Galaxies classified as E0 Galaxy appear to be almost perfect circles (ellipse). Elliptical galaxies have a broader range size than other types of galaxies. The smallest galaxies are dwarf elliptical galaxies, which is less than 10 percent the size of the Milky Way, and could contain only 10 million times the mass of the sun. Some ellipticals can also be stretched to more than a million light-years across, that can contain more than ten trillion stars. M87 (Messier 87) is identified as one of the largest galaxies in the universe. But astronomers have found more spiral galaxies than elliptical galaxies. As spiral galaxies are bright, elliptical galaxies are dim. Elliptical galaxies contain less gas and dust, which means few new stars are born.